Mouse CD279 Protein, His Tag
-
产品编号
KMP2367
-
别名
程序性死亡分子, Programmed cell death protein 1
-
规格
- 50ug
- 100ug
- 200ug
| Catalog Number | KMP2367 |
| Alias | 程序性死亡分子, Programmed cell death protein 1 |
| Size | 50ug, 100ug, 200ug |
| Product Description | The Mouse CD279 Protein(KMP2367) is produced in HEK293 Cells and the target gene encoding Leu25-Gln167 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Molecular Name | CD279 |
| Product Introduction | CD279(PD-1):免疫球蛋白超家族(IgSF)成员,通过跨膜形式参与T细胞功能调控。 |
| Molecular Weight | 16.15 kDa |
| Expression System | HEK293 Cells |
| Species | Mouse |
| Purity | >95% |
| SDS-PAGE | 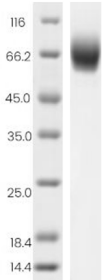 |
| Purification | Affinity Purification |
| Uniprot ID | Q02242 |
| Storage Condition | Aliquot and store at -20℃ to -80℃. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing cycles. |
| Formulation | 20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, pH8.0 |
| Shipping Condition | In general, the proteins are provided as lyophilized powder which are shipped at ambient temperature. They are shipped out in dry ice if supplied in liquid form. |
| Background | Programmed Death-1(PD-1), firstly cloned from mouse T cell hybridoma 2B4.11, is one member of CD28/CTLA-4 superfamily. PD-1 belongs to type I transmembrane protein and acts as an important immunosuppressive molecule. The cytoplamsic tail of PD-1 contains two structural motifs, an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif(ITIM) and an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif(ITSM) formed by two tyrosine residues which make the difference in PD-1 signal mediating. Mouse PD-1 is expressed in thymus and shares about 69% aa sequence identity with human PD-1. Recently, programmed death-1(PD-1) with its ligands, programmed death ligand B7H1(PD-L1) and B7DC(PD-L2), was found to regulate T-cell activation and tolerance, upon ligand binding, inhibiting T-cell effector functions in an antigen-specific manner. PD-1 gene knocked out mice would induce some autoimmune diseases, which suggests that PD-1 acts as a co-inhibitory molecule actively participating in maintaining peripheral tolerance. Thus, PD-1 may be a useful target for the immunologic therapy of carcinoma,infection,autoimmune diseases as well as organ transplantation. |
| Endotoxin | <1.0 EU/ug determined by the LAL method |
| Product Declaration | 该产品仅供科研使用,不可直接用于人体或注射。 |
蛋白可以在-80°C下储存以便长期保存。应分装并避免冻融循环,以保持蛋白的稳定性。
可以通过优化质粒设计、使用高效转染试剂、优化细胞培养条件以及使用蛋白折叠伴侣或密码子优化来提高蛋白表达效率。



 0
0
