Mouse CD150 Protein, His Tag
-
产品编号
KMP2417
-
别名
信号淋巴细胞激活分子家族成员 1, Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule, CD150
-
规格
- 50ug
- 100ug
- 200ug
| Alias | 信号淋巴细胞激活分子家族成员 1, Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule, CD150 |
| Catalog Number | KMP2417 |
| Product Description | The Mouse CD150 Protein(KMP2417) is produced in HEK293 Cells and the target gene encoding Thr25-Pro242 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Molecular Name | CD150 |
| Species | Mouse |
| Host | HEK293 Cells |
| Size | 50ug, 100ug, 200ug |
| Purity | >95% as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
| Endotoxin | <1.0 EU/ug determined by the LAL method |
| Formulation | PBS, pH7.4 |
| Background | Signaling lymphocyte activation molecule(SLAM), is a self-ligand glycoprotein which exists not only found on the surface of activated and memory T cells, but also on the surface of activated B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. SLAM consists of a extracellular domain(ECD) with two Ig-like domains,transmembrane segment, and cytoplasmic domain with three immunoreceptor tyrosine switch motifs(ITSM). SLAM is thought to play an important role in adhesion between T cells and APCs and has been shown to act as a coreceptor in TCR-dependent responses. SLAM, together with CD46, is one of the two receptors for measles virus. SLAM is a cell surface receptor that, like the B cell receptor, CD40, and CD95, can transmit positive or negative signals. SLAM can associate with the SH2-containing inositol phosphatase(SHIP), the SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase(SHP-2), and the adaptor protein SH2 domain protein 1A. It’s upregulated on activated B cells and CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, but downregulated on Th2 polarized cells. Also, it can Inhibits antigen receptor-mediated production of IFN-gamma, but not IL-2, in CD4-/CD8- T-cells |
| SDS-PAGE | 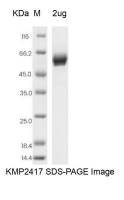 |
| Predicted Molecular Weight | 25.01 kDa |
| Storage Condition | Aliquot and store at -20℃ to -80℃. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing cycles. |
| Shipping Condition | In general, the proteins are provided as lyophilized powder which are shipped at ambient temperature. They are shipped out in dry ice if supplied in liquid form. |
| Uniprot ID | Q9QUM4 |
| References | 1.Nat. Immunol. 2:681-690 (2001) 2.J. Exp. Med. 199:1255-1264 (2004) 3.Blood 104:4063-4070 (2004) 4.Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 35:206-210 (2006) 5.Front. Immunol. 6:158-158 (2015) 6.Nat. Immunol. 11:920-927 (2010) 7.J. Biol. Chem. 287:18359-18365 (2012) |
| Function | Self-ligand receptor of the signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM) family. SLAM receptors triggered by homo- or heterotypic cell-cell interactions are modulating the activation and differentiation of a wide variety of immune cells and thus are involved in the regulation and interconnection of both innate and adaptive immune response. Activities are controlled by presence or absence of small cytoplasmic adapter proteins, SH2D1A/SAP and/or SH2D1B/EAT-2. SLAMF1-induced signal-transduction events in T-lymphocytes are different from those in B-cells. Two modes of SLAMF1 signaling seem to exist: one depending on SH2D1A (and perhaps SH2D1B) and another in which protein-tyrosine phosphatase 2C (PTPN11)-dependent signal transduction operates. Initially it has been proposed that association with SH2D1A prevents binding to inhibitory effectors including INPP5D/SHIP1 and PTPN11/SHP-2 (By similarity). However, signaling is also regulated by SH2D1A which can simultaneously interact with and recruit FYN which subsequently phosphorylates and activates SLAMF1 (By similarity). Mediates IL-2-independent proliferation of activated T-cells during immune responses and induces IFN-gamma production (PubMed:9126961, PubMed:12351401). Downstreaming signaling involves INPP5D, DOK1 and DOK2 leading to inhibited IFN-gamma production in T-cells, and PRKCQ, BCL10 and NFKB1 leading to increased T-cell activation and Th2 cytokine production. Promotes T-cell receptor-induced IL-4 secretion by CD4+ cells. Inhibits antigen receptor-mediated production of IFN-gamma, but not IL-2, in CD4-/CD8- T-cells. Required for IL-4 production by germinal centers T follicular helper (T(Fh))cells. May inhibit CD40-induced signal transduction in monocyte-derived dendritic cells (By similarity). May play a role in allergic responses and may regulate allergen-induced Th2 cytokine and Th1 cytokine secretion. In conjunction with SLAMF6 controls the transition between positive selection and the subsequent expansion and differentiation of the thymocytic natural killer T (NKT) cell lineage. Involved in the peripheral differentiation of indifferent natural killer T (iNKT) cells toward a regulatory NKT2 type. In macrophages involved in down-regulation of IL-12, TNF-alpha and nitric oxide in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS). In B-cells activates the ERK signaling pathway independently of SH2D1A but implicating both, SYK and INPP5D, and activates Akt signaling dependent on SYK and SH2D1A. In conjunction with CD84/SLAMF5 and SLAMF6 may be a negative regulator of the humoral immune response. (Microbial infection) Involved in innate immune response against Gram-negative bacteria in macrophages; probably recognizes OmpC and/or OmpF on the bacterial surface, regulates phagosome maturation and recruitment of the PI3K complex II (PI3KC3-C2) leading to accumulated of PdtIns3P and NOX2 activity in the phagosomes . |



 0
0
