Human CD152 Protein, GST Tag
-
产品编号
KMP2326
-
别名
细胞毒T淋巴细胞相关抗原, Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4, CD152
-
规格
- 50ug
- 100ug
- 200ug
| Alias | 细胞毒T淋巴细胞相关抗原, Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4, CD152 |
| Catalog Number | KMP2326 |
| Product Description | The Human CD152 Protein(KMP2326) is produced in HEK293 Cells and the target gene encoding Lys36-Asp161 is expressed with a GST tag at the C-terminus. |
| Molecular Name | CD152 |
| Species | Human |
| Host | HEK293 Cells |
| Size | 50ug, 100ug, 200ug |
| Purity | >95% as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
| Endotoxin | <1.0 EU/ug determined by the LAL method |
| Formulation | PBS, pH7.4 |
| Background | Cytotoxic Tlymphocyte 4(CTLA-4,CD152), is a type I transmembrane T cell inhibitory molecule that is a member of the Ig superfamily. Human or mouse CTLA4 cDNA encodes 223 amino acids(aa) including a 35 aa signal sequence, a 126 aa extracellular domain(ECD) with one Ig-like V-type domain, a 21 aa transmembrane(TM) sequence, and a 41 aa cytoplasmic sequence.It is widely expressed with highest levels in lymphoid tissues. CD28 and CTLA-4, together with their ligands, B7-1 and B7-2, constitute one of the dominant costimulatory pathways that regulate T and B cell responses. CD28 and CTLA-4 are structurally homologous molecules that are members of the immunoglobulin(Ig) gene superfamily. CTLA4 transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells, whereas CD28 transmits a stimulatory signal. Intracellular CTLA4 is also found in regulatory T Cells and may play an important role in their functions. Tcell activation through the Tcell receptor and CD28 leads to increased expression of CTLA4. |
| SDS-PAGE | 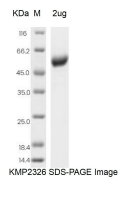 |
| Predicted Molecular Weight | 40.48 kDa |
| Storage Condition | Aliquot and store at -20℃ to -80℃. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing cycles. |
| Shipping Condition | In general, the proteins are provided as lyophilized powder which are shipped at ambient temperature. They are shipped out in dry ice if supplied in liquid form. |
| Uniprot ID | Q6GTX8 |
| References | 1.J. Immunol. 162:5800-5804 (1999) 2.J. Biol. Chem. 275:17440-17446 (2000) 3.Eur. J. Immunol. 30:2751-2758 (2000) 4.Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 12:705-712 (2005) 5.Eur. J. Immunol. 36:190-198 (2006) 6.Eur. J. Immunol. 28:2086-2091 (1998) |
| Function | Functions as an inhibitory receptor that plays a constitutive negative regulatory role on cytolytic function of natural killer (NK) cells, B-cells and T-cells. Activation by Tyr phosphorylation results in recruitment and activation of the phosphatases PTPN6 and PTPN11. It also reduces the increase of intracellular calcium evoked by B-cell receptor ligation. May also play its inhibitory role independently of SH2-containing phosphatases. Modulates cytokine production in CD4+ T-cells, down-regulating IL2 and IFNG production while inducing secretion of transforming growth factor beta. Down-regulates also IgG and IgE production in B-cells as well as IL8, IL10 and TNF secretion. Inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in myeloid leukemia cell lines as well as prevents nuclear translocation of NF-kappa-B p65 subunit/RELA and phosphorylation of I-kappa-B alpha/CHUK in these cells. Inhibits the differentiation of peripheral blood precursors towards dendritic cells. |



 0
0
