Human INDO Protein, His Tag
-
产品编号
KMP2319
-
别名
吲哚 2, 3-二氧合酶 , Indole 2, 3-dioxygenase, INDO
-
规格
- 50ug
- 100ug
- 200ug
| Alias | 吲哚 2, 3-二氧合酶 , Indole 2, 3-dioxygenase, INDO |
| Catalog Number | KMP2319 |
| Product Description | The Human INDO Protein(KMP2319) is produced in E.coli and the target gene encoding Met1-Gly403 is expressed with a 6His tag at the N-terminus. |
| Molecular Name | INDO |
| Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Size | 50ug, 100ug, 200ug |
| Purity | >95% as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
| Endotoxin | <1.0 EU/ug determined by the LAL method |
| Formulation | 20mM Sodium Acetate, 150mM NaCl and 20% Glycerol, pH4.5 |
| Background | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase(IDO) is a heme enzyme that initiates the oxidative degradation of the least abundant, essential amino acid, l-tryptophan, along the kynurenine pathway. This protein is normally expressed in the dendritic cells, macrophages, microglia, eosinophils, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and most tumor cells. IDO activity is associated with immunosuppression and immune attenuation. Several studies showed that IDO can contribute to immune escape when expressed directly in tumor cells or when expressed in immunosuppressive antigen presenting cells such as tolerogenic dendritic cells or tumor associated macrophages. IDO also is a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of cancer, chronic viral infections, and other diseases characterized by pathological immune suppression. |
| SDS-PAGE | 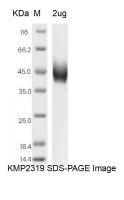 |
| Predicted Molecular Weight | 46.16 kDa |
| Storage Condition | Aliquot and store at -20℃ to -80℃. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing cycles. |
| Shipping Condition | In general, the proteins are provided as lyophilized powder which are shipped at ambient temperature. They are shipped out in dry ice if supplied in liquid form. |
| Uniprot ID | P14902 |
| References | 1.Nat. Med. 9:1269-1274 (2003) 2.Cancer Res. 67:7082-7087 (2007) 3.Trends Immunol. 34:137-143 (2013) 4.Front. Immunol. 5:384-384 (2014) 5.Front. Immunol. 6:34-34 (2015) 6.J. Med. Chem. 58:9421-9437 (2015) 7.Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 58:153-157 (2009) 8.Exp. Mol. Med. 46:E121-E121 (2014) 9.FEBS J. 282:2735-2745 (2015) 10.Cancer Res. 67:7082-7087 (2007) |
| Function | Catalyzes the first and rate limiting step of the catabolism of the essential amino acid tryptophan along the kynurenine pathway (PubMed:17671174). Involved in the peripheral immune tolerance, contributing to maintain homeostasis by preventing autoimmunity or immunopathology that would result from uncontrolled and overreacting immune responses (PubMed:25691885). Tryptophan shortage inhibits T lymphocytes division and accumulation of tryptophan catabolites induces T-cell apoptosis and differentiation of regulatory T-cells (PubMed:25691885). Acts as a suppressor of anti-tumor immunity (PubMed:23103127, PubMed:25157255, PubMed:14502282, PubMed:25691885). Limits the growth of intracellular pathogens by depriving tryptophan (PubMed:25691885). Protects the fetus from maternal immune rejection (PubMed:25691885). IDO1 is the target for therapy in a range of clinical settings, including cancer, chronic infections, autoimmune and allergic syndromes, and transplantation. IDO1 and IDO2 are 2 distinct enzymes which catalyze the same reaction. IDO2 affinity for tryptophan is much lower than that of IDO1. 50% of Caucasians harbor polymorphisms which abolish IDO2 enzymatic activity. IDO2 is expressed in human tumors in an inactive form: tryptophan degradation is entirely provided by IDO1 in these cells (PubMed:18418598). IDO2 may play a role as a negative regulator of IDO1 by competing for heme-binding with IDO1 (PubMed:25394548). Low efficiency IDO2 enzymes have been conserved throughout vertebrate evolution, whereas higher efficiency IDO1 enzymes are dispensable in many lower vertebrate lineages (PubMed:25950090). IDO1 may have arisen by gene duplication of a more ancient proto-IDO gene before the divergence of marsupial and eutherian (placental) mammals Elevated IDO1 expression is a hallmark of major viral infections including HIV, HBV, HCV or influenza and also of major bacteria infections, such as Tb, CAP, listeriosis and sepsis. Depletion of tryptophan and production of tryptophan metabolites with bactericidal activity are important as direct anti-pathogen mechanisms. Pathogens are able to highjack the immunosuppressive effects of IDO1 and make use of them to facilitate their own life cycle.D-tryptophan + O2 = N-formyl-D-kynurenine Activity is inhibited by and MTH-trp (methylthiohydantoin-DL-tryptophan), modestly inhibited by L-1MT (1-methyl-L-tryptophan) but not D-1MT (1-methyl-D-tryptophan). |



 0
0
