Mouse CD137L Protein, His Tag
-
产品编号
KMP2316
-
别名
肿瘤坏死因子配体超家族成员 9, CD137L, TNFSF9
-
规格
- 50ug
- 100ug
- 200ug
| Alias | 肿瘤坏死因子配体超家族成员 9, CD137L, TNFSF9 |
| Catalog Number | KMP2316 |
| Product Description | The Mouse CD137L Protein(KMP2316) is produced in HEK293 Cells and the target gene encoding Arg104-Glu309 is expressed with a 10His tag at the N-terminus. |
| Molecular Name | CD137L |
| Species | Mouse |
| Host | HEK293 Cells |
| Size | 50ug, 100ug, 200ug |
| Purity | >90% as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
| Endotoxin | <1.0 EU/ug determined by the LAL method |
| Formulation | PBS, pH7.4 |
| Background | Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 9, also known as 4-1BBL, is a member of the the tumor necrosis factor family. Mouse 4-1BBL cDNA encodes a 309 amino acid residues(aa) protein with an 82 aa N-terminal cytoplasmic domain, a 21 aa transmembrane domain and a 206 aa C-terminal extracellular domain. The extracellular domain of 4-1BBL has a tertiary structure similar to that of other TNFSF members, but shares only low aa sequence homology(14-16%). 4-1BBL is predominantly expressed on activated antigen presenting cells(APCs) such as B cells, macrophages and dendritic cells(DCs). It is also expressed on most T and B lymphoma cell lines. TNFSF9 has been shown to reactivate anergic T lymphocytes in addition to promoting T lymphocyte proliferation. This cytokine has also been shown to be required for the optimal CD8 responses in CD8 T cells, and is thought to be involved in T cell-tumor cell interaction. |
| SDS-PAGE | 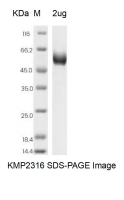 |
| Predicted Molecular Weight | 22.97 kDa |
| Storage Condition | Aliquot and store at -20℃ to -80℃. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing cycles. |
| Shipping Condition | In general, the proteins are provided as lyophilized powder which are shipped at ambient temperature. They are shipped out in dry ice if supplied in liquid form. |
| Uniprot ID | P41274 |
| Function | Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF9. Induces the proliferation of activated peripheral blood T-cells. May have a role in activation-induced cell death (AICD). May play a role in cognate interactions between T-cells and B-cells/macrophages. |



 0
0
